What is DMZ and how to configure DMZ host?
DMZ in a router is a function that allows you to open all external ports for a specific IP from the router's local network. Usually used to implement remote access to a specific device behind the router. Especially often DMZ is used to access from anywhere in the Internet to IP cameras or DVR, i.e. for video surveillance.
Sponsored
Many Wi-Fi routers have the function of providing access from an external network to devices on their local network (DMZ host mode, it is also the exposed host). In this mode, the device (computer, DVR, IP camera, etc.) in the local network all ports are open. A DMZ host can freely connect to resources on the internal network, while connections to the internal network from the canonical DMZ are blocked by the firewall that separates them.
Pros and Cons of using a DMZ in a router
Pros of using a DMZ in a router:
- Improved security: By placing servers and other sensitive resources in a DMZ, you can better protect them from external threats such as hackers and malware. The DMZ acts as a buffer between the internal network and the internet, allowing you to more easily monitor and control access to your internal resources.
- Enhanced privacy: DMZs can help to prevent unauthorized access to your internal network and the sensitive data it contains. This is especially important if you have servers or other resources that contain sensitive information, such as financial records or personal data.
- Improved performance: DMZs can help to improve the performance of your network by offloading some of the traffic that would normally be handled by your internal servers. This can help to reduce the load on your internal network and improve the overall performance of your network.
- Simplified network management: By separating your internal resources from the internet, a DMZ can help to simplify network management. This is because you can more easily monitor and control access to your internal resources, which can make it easier to identify and address potential security issues.
Cons of using a DMZ in a router:
- Reduced security: While a DMZ can provide an additional layer of security for your internal network, it is important to note that the DMZ itself is not secure. It is still exposed to external threats such as hackers and malware, and servers or other resources placed in the DMZ may be more vulnerable to attack.
- Complexity: Setting up and maintaining a DMZ can be complex, especially for larger networks with many servers and other resources. This can require additional hardware and software resources, as well as specialized knowledge and expertise.
- Limited flexibility: DMZs can be inflexible, as they typically require the use of static IP addresses and cannot easily accommodate changes to the network configuration. This can make it difficult to quickly and easily make changes to the network or add new resources.
- Performance issues: Depending on the size and complexity of your network, a DMZ may introduce additional latency or other performance issues. This can be especially true if the DMZ is handling a large volume of traffic or if it is not properly configured.
Configure DMZ Host in TP-Link Router
SponsoredStep 1: Login to the management page
Open the web browser and type the IP address of the device in the address bar (default is 192.168.1.1/192.168.0.1/192.168.0.254). Press Enter.
The default username and password are both admin. Click OK to log into the device.
Step 2: Configure the DMZ
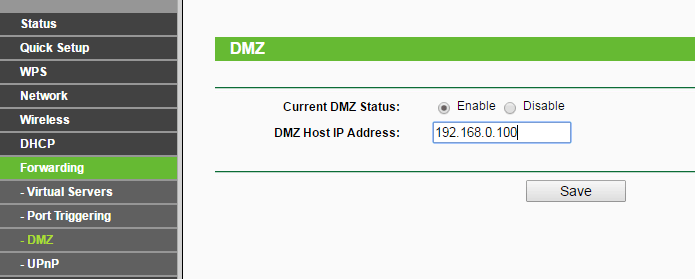
Once you are done with DMZ host configuration. You can now test open ports by going to portcheckers.com home page.